Deep Geometrized Cartoon Line Inbetweening: A New Approach to Anime Frame Interpolation

In the field of anime production, a significant yet understudied challenge has been the inbetweening of cartoon line drawings. Inbetweening, the process of generating intermediate frames between two black-and-white line drawings, is a labor-intensive and costly procedure that has long been sought for automation. A recent study Deep Geometrized Cartoon Line Inbetweening by Li Siyao and team from Nanyang Technological University, Lexica, and Southeast University, offers a novel approach to this challenge.
The Problem at Hand
Despite the advancements in cartoon animation since its inception in the early 1900s, the core element of line drawings still requires manual intervention. The process of inbetweening, or creating intermediate frames between two key drawings, is particularly labor-intensive. Traditional frame interpolation methods, which rely on matching and warping entire raster images, often produce blurring artifacts, especially when applied to the intricate structures of line drawings.
Introducing AnimeInbet
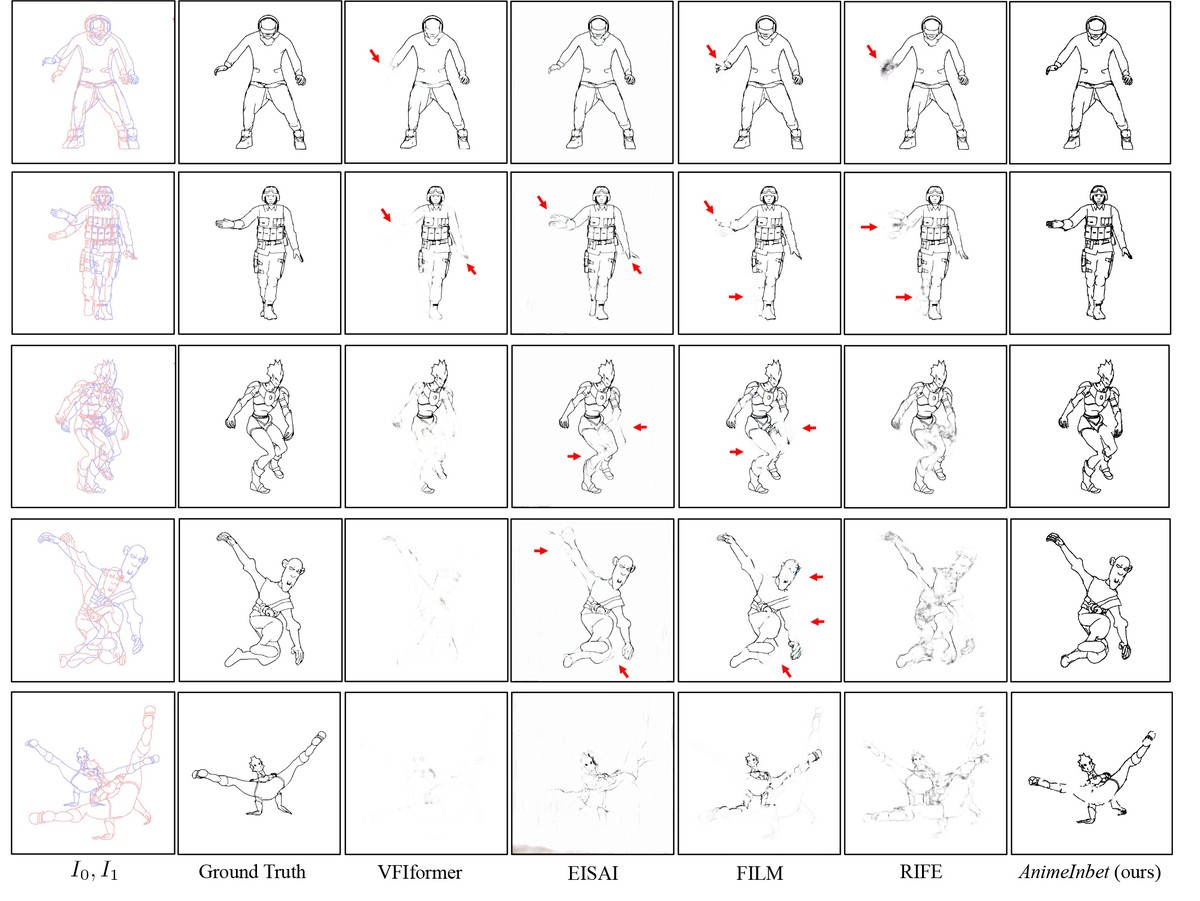
To address the limitations of existing methods, the researchers introduced AnimeInbet, a new approach that transforms raster line drawings into graphs of endpoints. This method reframes the inbetweening task as a graph fusion problem with vertex repositioning. By focusing on the unique structure of line drawings, AnimeInbet can effectively capture the sparsity and preserve the details during the inbetweening process.
The core idea behind AnimeInbet is to identify matching vertices between two input line drawing graphs and then reposition them to create a new intermediate graph. The method employs a vertex encoding strategy, a vertex correspondence Transformer, and a visibility predictor to achieve this.
MixamoLine240: A New Dataset
To train and evaluate AnimeInbet, the researchers introduced MixamoLine240, a new dataset of line drawings with ground truth vectorization and matching labels. This dataset provides both raster line drawings and accurate labels for each frame, offering a comprehensive training ground for the new method.
The dataset was created using the "Cel-shading" technique, which renders 3D resources into an anime-style appearance. The researchers used the open-source 3D material library Mixamo to select 20 characters and 20 actions, resulting in a diverse set of data.
How AnimeInbet Works
AnimeInbet's framework consists of four main parts:
1. Vertex Geometric Embedding: This encodes the vertices of the line drawings into distinguishable features.
2. Vertex Correspondence Transformer: It aggregates the mutuality of vertex features to determine the correspondence between vertices of two input drawings.
3. Repositioning Propagation: This step involves propagating the vertex shifts from matched vertices to unmatched ones.
4. Graph Fusion: The final step superposes the two input graphs based on the predicted correspondence and refines the output by predicting visibility maps.
The introduction of AnimeInbet marks a significant step forward in automating one of the most labor-intensive processes in art production. By focusing on the unique challenges posed by line inbetweening, the method offers a promising solution that outperforms existing solutions. With the added benefit of the MixamoLine240 dataset, researchers and practitioners now have a robust toolset to further advance the field of anime production.